Compounding machinery for Polyisobutylene (PIB) for technical applications
Polyisobutylene (PIB) belongs to the polymer family of olefins. It has been produced industrially since the 1930’s and is available in wide-ranging viscosities from oily to rubbery. Its mechanical properties depend strongly on the mean molar mass. Special features include the excellent electrical insulating properties and dielectric values, very good resistance to acids, alkalis and salt solutions, and very low water vapour and gas permeabilities.
Typical applications
Based on its properties, PIB (Polyisobutylene) is used as the key formulation component for various applications. For example, its corrosion resistance is important for tank linings or pipe jacketing. PIB is highly regarded for joint and web seals. This is due to its applicability over a wide temperature range including very low temperatures (down to -50 ° C). The adjustable tackiness is used in both foil/film and hot glue applications. For packaging, especially in the food industry, its gas impermeability is ideal.
Polyolefin masterbatches containing 60+% of PIB can be produced for such applications as stretch film for food wrap, pallet wrap and other applications. Due to the physical nature of PIB (Polyisobutylene), it is not easy to work with, so masterbatches provide the market with an easy to utilize masterbatch pellet which can be let down into the percentage that is optimal for the particular application.
Compounding requirements
Its wide range of possible uses and excellent compatibility with other plastics also result in challenging compounding tasks. Thus, the stickiness or the cold-flow properties of PIB (Polyisobutylene) can already be a demanding challenge when dosing and feeding to the compounding line in the compounding machinery. Sophisticated procedures are used to accommodate and meet these high demands. The BUSS Kneader can make the most its specific strengths by comparison with alternative systems: the moderate and adjustable shear rates dissipate the melting energy very efficiently, and a broad viscosity field is easily mastered. Due to the enormous number of mixing cycles, the highest proportions of aggregates such as carbon black or graphite can be controlled very well in the mixing zones by the BUSS compounding machinery.
The BUSS Kneader’s two-stage system deliberately separates the compounding and pressure build-up stages so that each stage can be independently optimized. For PIB compounds the appropriate pressure build-up element is selected according to application. Either gear pumps can be used, e.g. for direct processing of foils/films, or a flanged extruder for pelletizing highly viscous and/or filled formulations. The hinged housing of the BUSS Kneader ensures fast access and high system availability. Together with broadly based BUSS compounding process expertise, the modular design and therefore adaptable arrangement of the entire compounding line make the BUSS Kneader an excellent choice for compounding technical PIB in all its diverse applications.

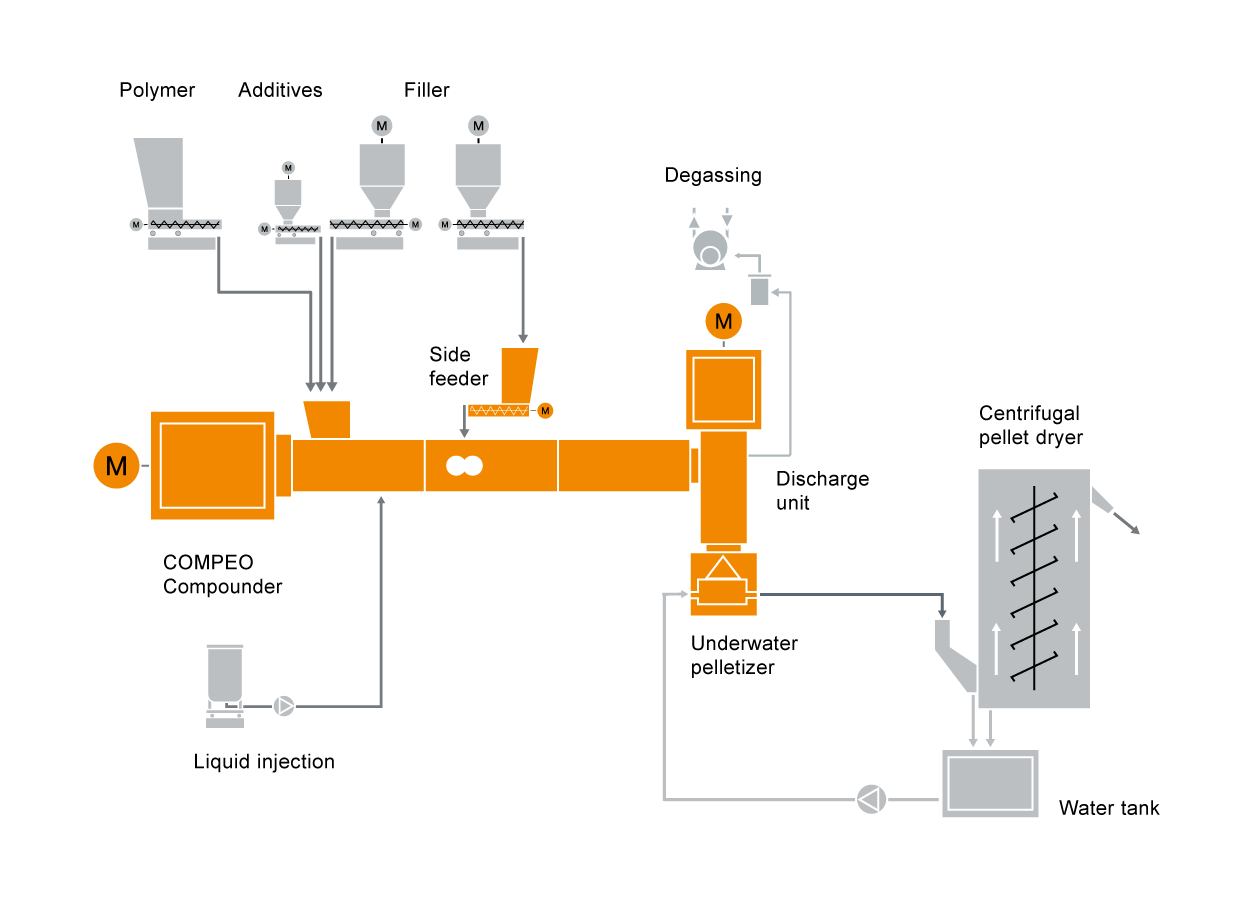
Typical compounding plant layout for PIB for technical applications
BUSS compounding systems offer the following specific benefits
Learn More
Downloads
-
COMPEO





